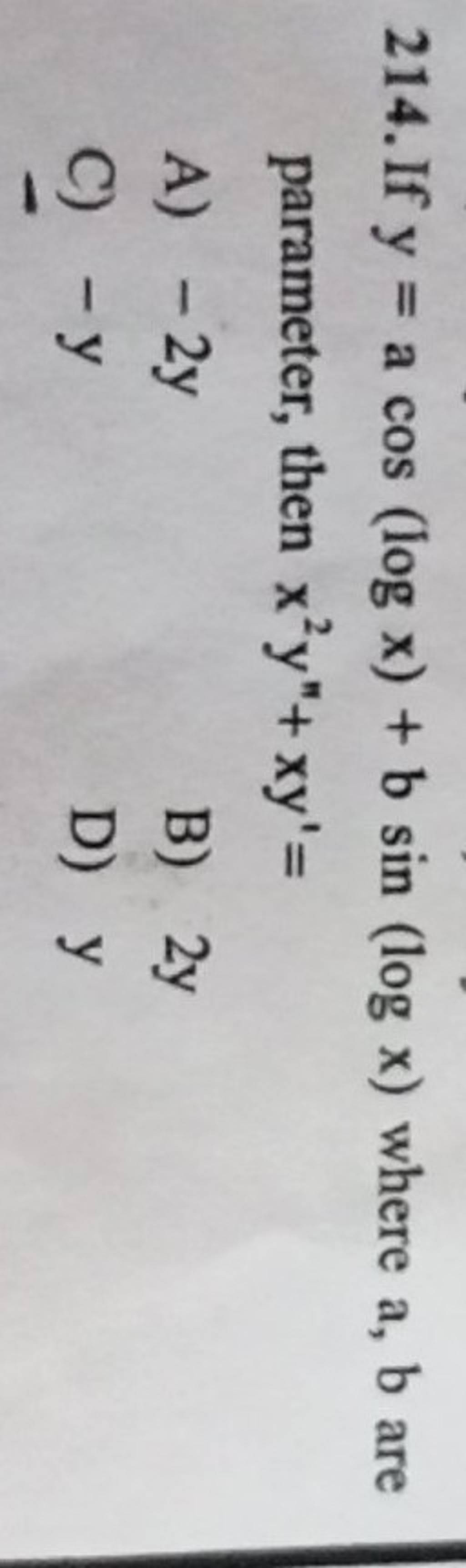How to prove that g(x) =(ln2) cos (pi.x) /2 +1/x has a root lying between 1 and 2 by applying a mean value theorem to f(x) =(ln2) sin (pi.x) /2 +logx -

Use a graphing utility to approximate the solutions of the equation in the interval [0, 2pi). sin(x + pi/2) - cos(x + 3pi/2) = 1. | Homework.Study.com















![intlogx.sin [ 1 + (logx)^2 ]/xdx intlogx.sin [ 1 + (logx)^2 ]/xdx](https://dwes9vv9u0550.cloudfront.net/images/4941372/17aa8d90-0883-4f60-b42e-d54e6cf8fbf7.jpg)